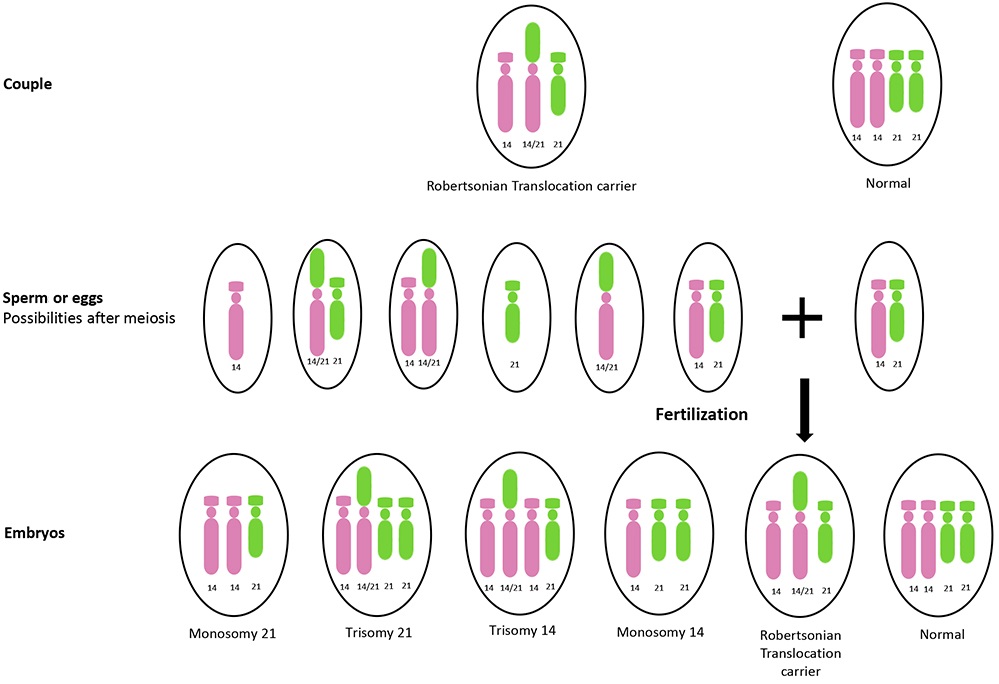
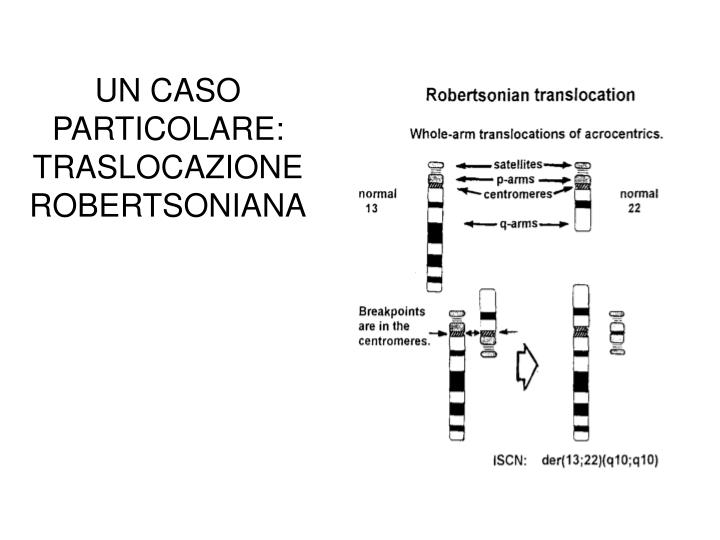
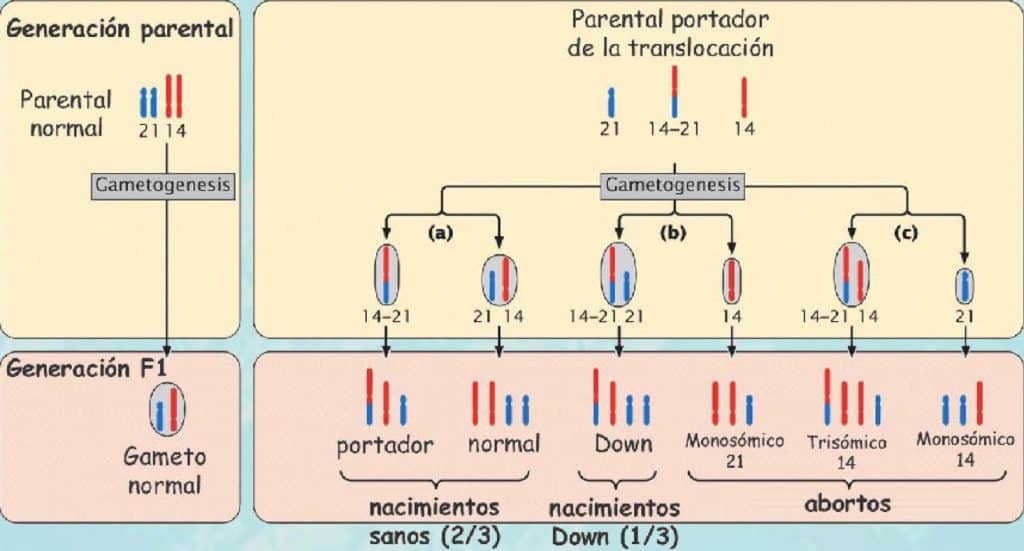
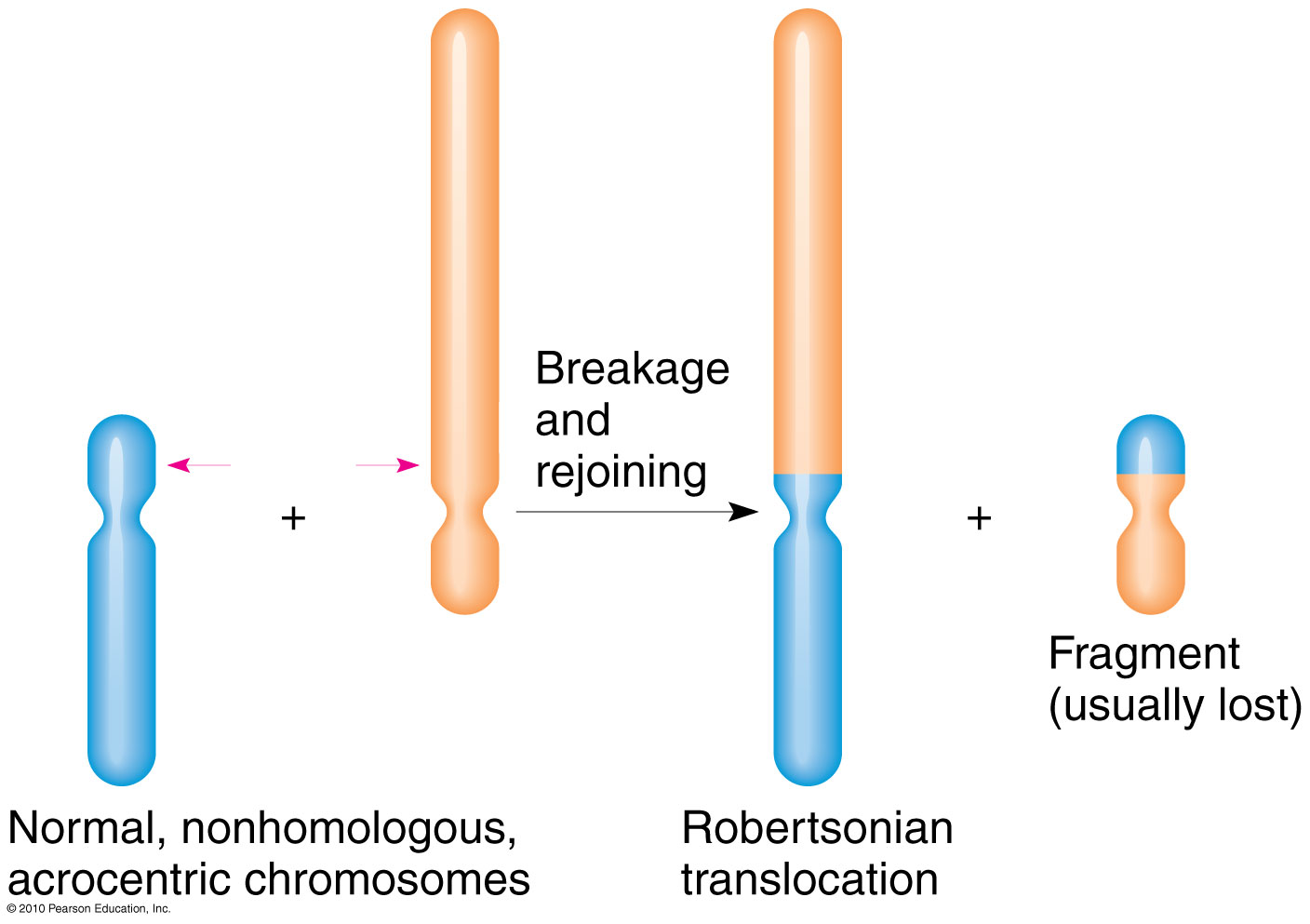
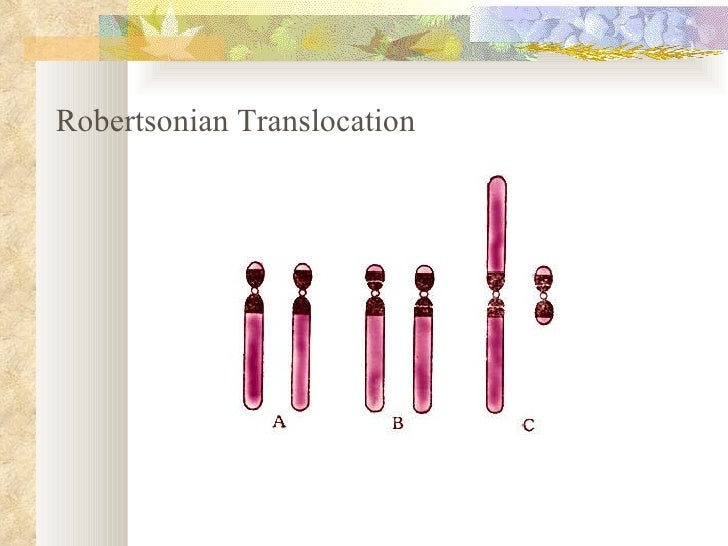
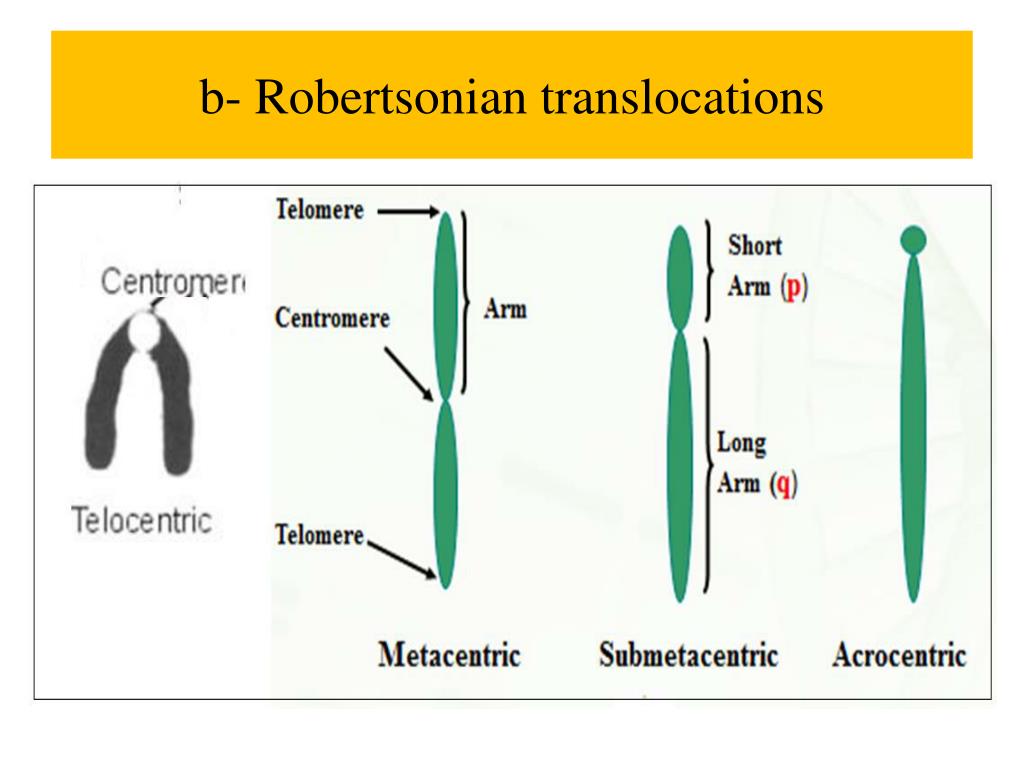
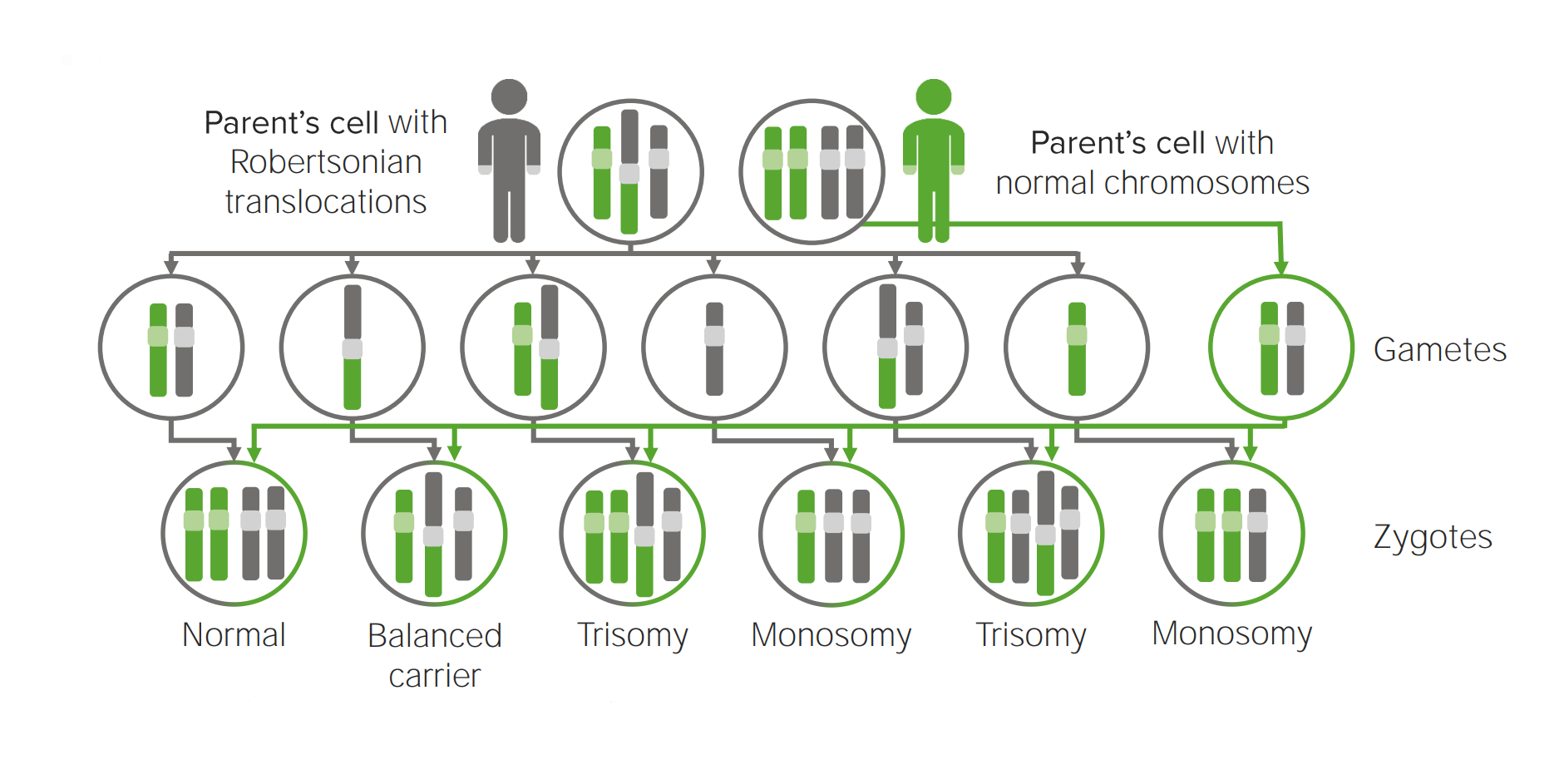
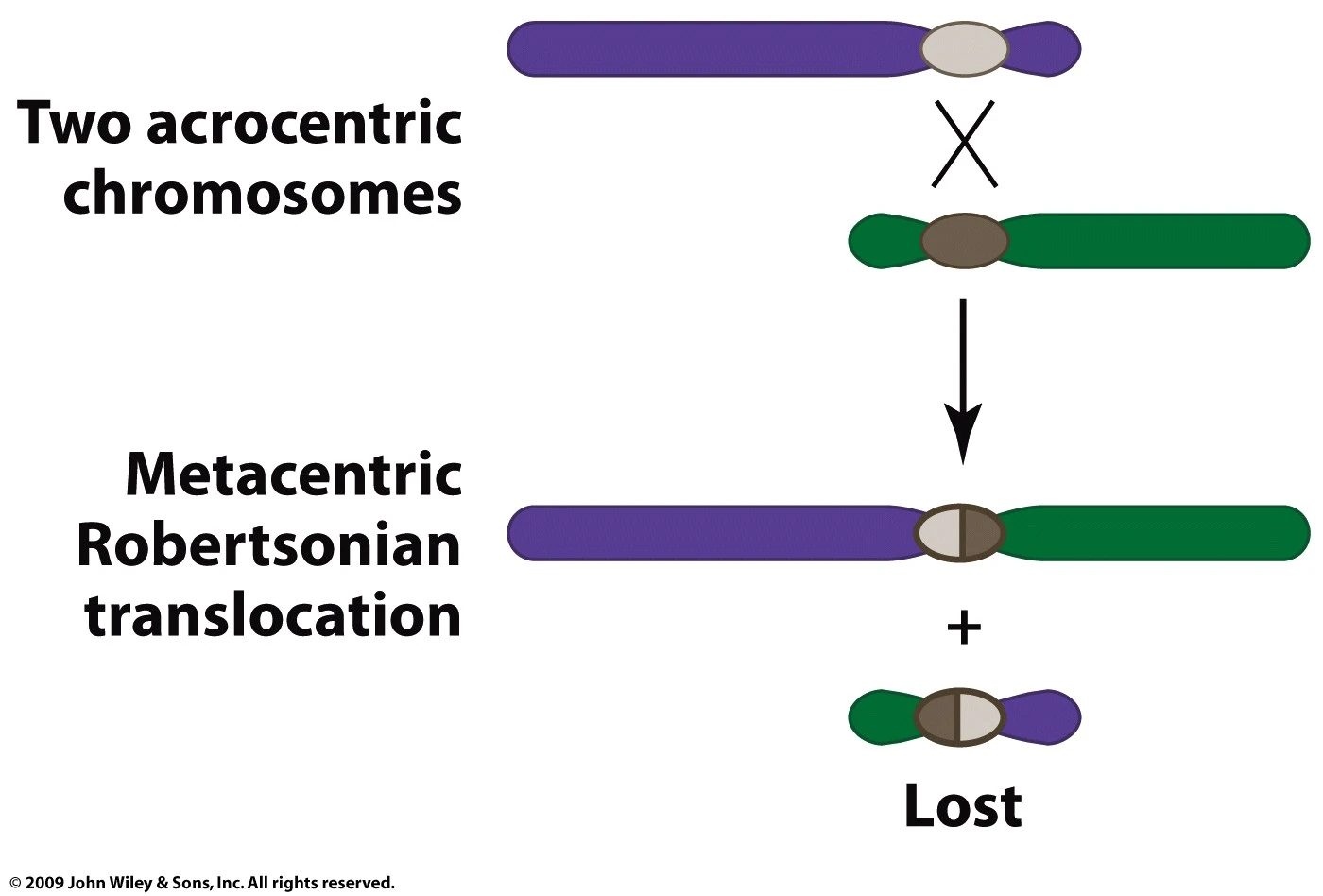
The most common Robertsonian translocation in humans is a 13/14 fusion chromosome. The cytogenetic designation of a balanced carrier is either 45,XY,rob(13;14) (q10;q10) or 45,XY,der(13;14) (q10;q10). This nomenclature means that there are 45 chromosomes in the cells with a normal male sex chromosome complement and a Robertsonian translocation.. Introduction. Robertsonian (rob) translocation is the most common form of structural chromosomal abnormality or rearrangement [1-3].One in 1,000 healthy individuals is thought to carry a Robertsonian translocation inherited from one of the parents with a normal phenotype [2-4].A Robertsonian translocation involves only the acrocentric chromosomes (13, 14, 15, 21, and 22).
Preimplantation Testing for Chromosomal Structural Rearrangements (PGTSR)

Investigating human genomes… Stowers Institute for Medical Research

Translocation (Chromosome Mutation) — Definition & Impact Expii
PPT ANOMALIE CROMOSOMICHE STRUTTURALI MUTAZIONI CROMOSOMICHE PowerPoint Presentation ID921089
El Síndrome de Down CURSO DE PEDIATRÍA Paradigmia
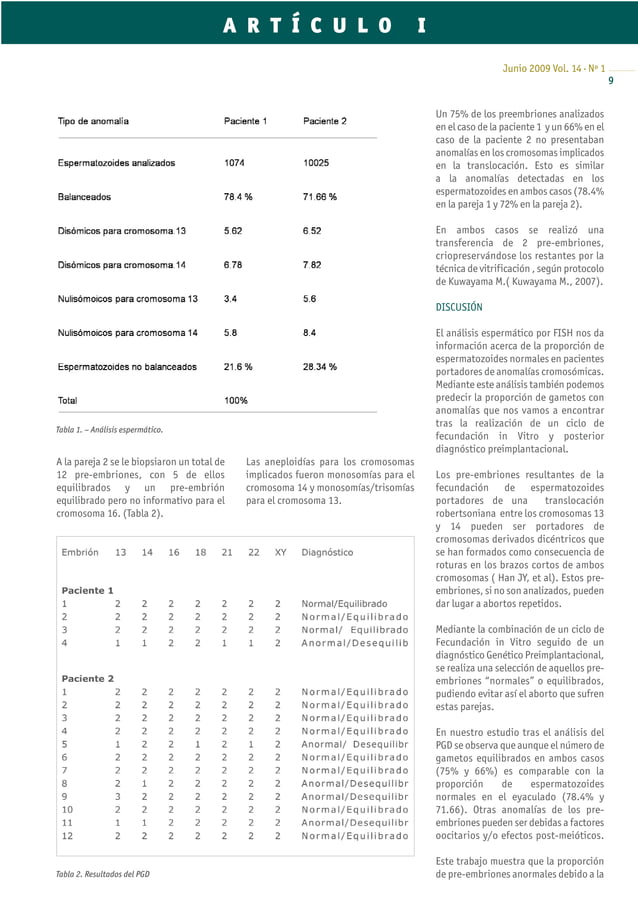
ESTUDIO GENÉTICO PREIMPLANTACIONAL EN PACIENTES PORTADORES DE TRANSLOCACIÓN ROBERTSONIANA (13;14)
Robertsonian Translocation 13 14
8 Chromosome Disorder
PPT Chromosomal Abnormalities II SDK November 3, 2012 PowerPoint Presentation ID2940097
Síndrome de Patau (Trissomia 13) Concise Medical Knowledge
Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13) Concise Medical Knowledge

Aberraciones por translocación robertsoniana YouTube
PPT INVERSIONI PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID193931

Translocação Robertsoniana YouTube

PPT Quando i cromosomi si rompono PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5188971
Translocation UVM & Genomics Wiki FANDOM powered by Wikia
PPT INVERSIONI PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID193931

Robertsonian Translocation 13 14

Robertsonian Translocation 13 14

question about robertsonian translocation r/Mcat
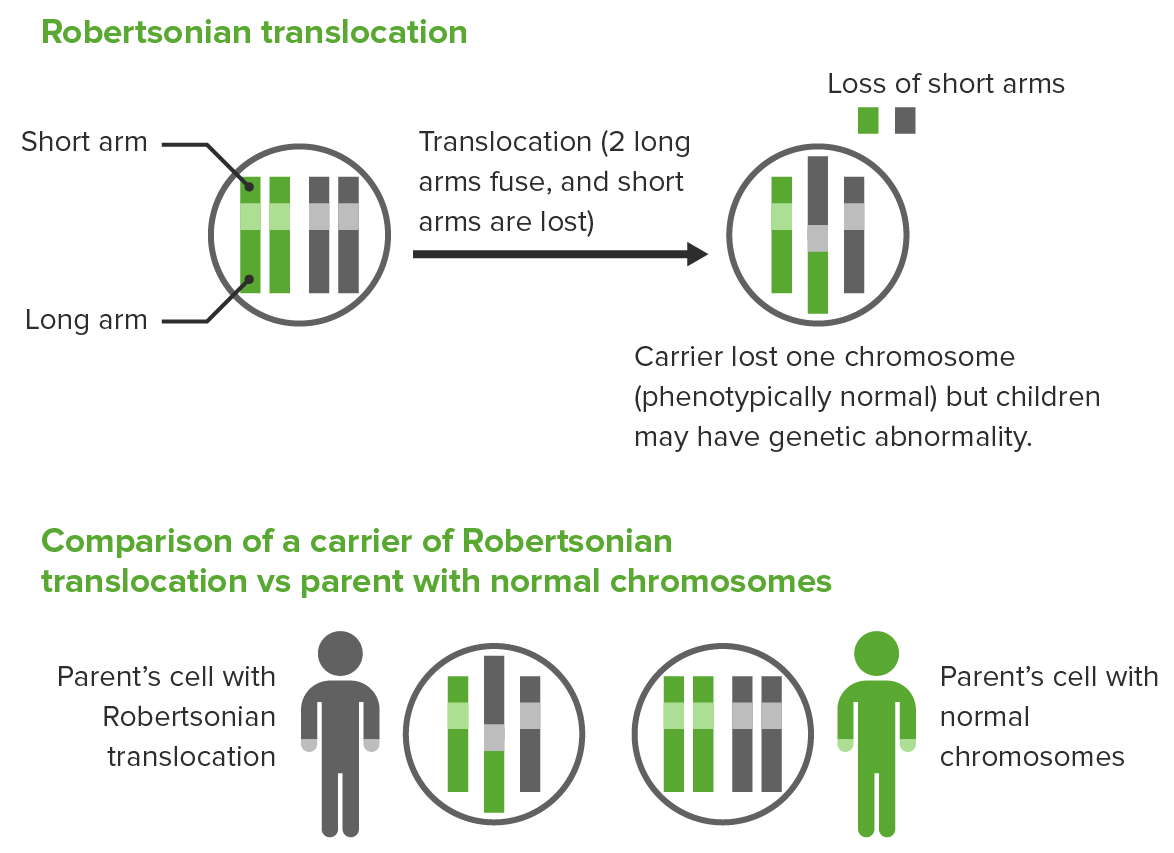
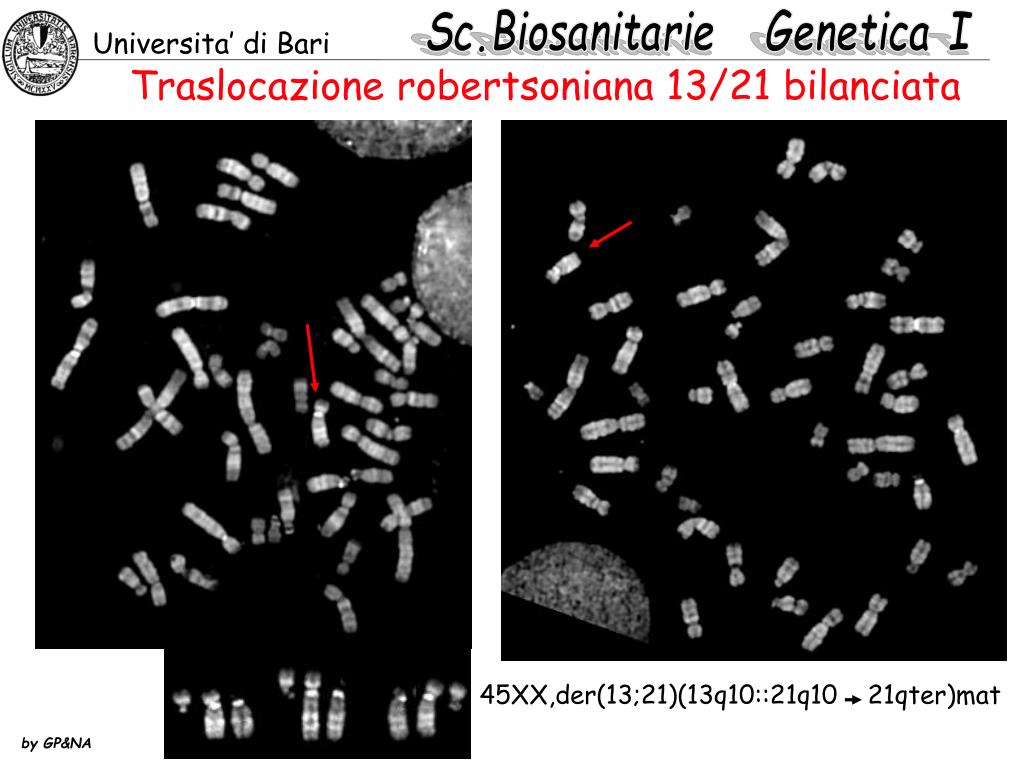
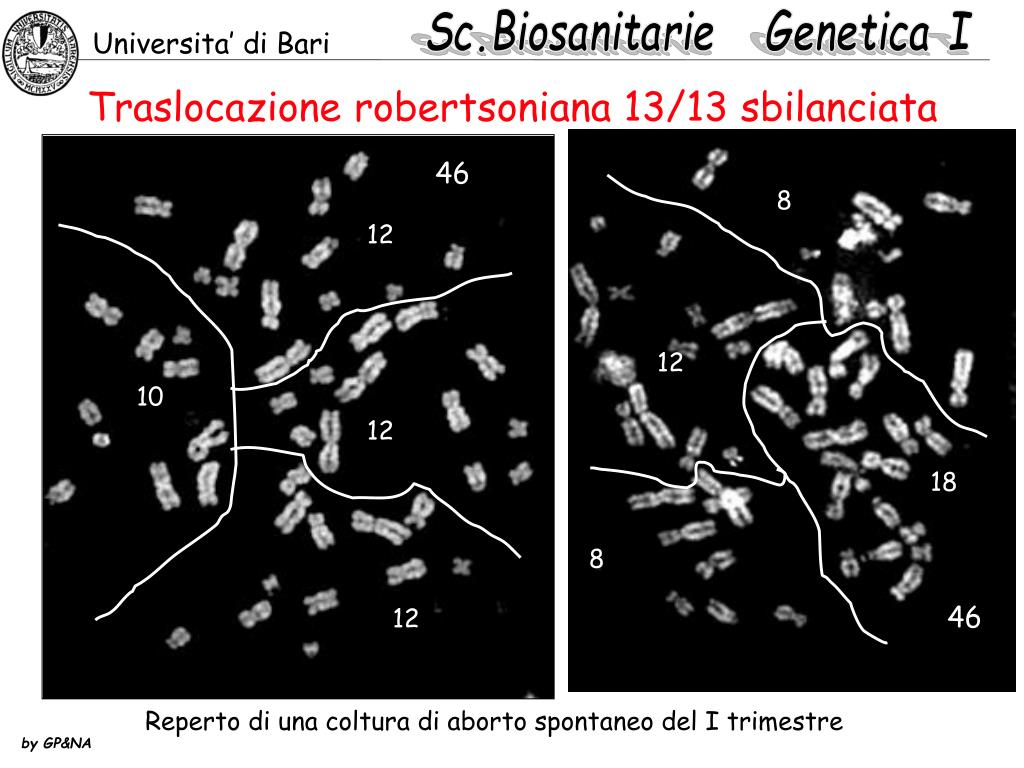
Robertsonian translocation ( ROB) is a chromosomal abnormality where the entire long arms of two different chromosomes become fused to each other. It is the most common form of chromosomal translocation in humans, affecting 1 out of every 1,000 babies born. [1] It does not usually cause medical problems, though some people may produce gametes.. La traslocazione robertsoniana t (13;14) (q10;q10), è bilanciata e determinata tra il braccio lungo di un cromosoma 13 ed il braccio lungo di un cromosoma 14. I problemi di chi porta tale traslocazione sono essenzialmente legati alla funzione riproduttiva, in quanto essi risultano a rischio di produrre gameti sbilanciati.